Tel: 01763 262333
Density Measurement – Pycnometry
Bulk / Envelope Density Measurement Absolute / True Density Measurement Skeletal & Particle Density Measurement
Density
is
an
important
physical
characteristic
of
solid
materials,
which
has
inextricable
links
to
porosity
and
direct
affects
the
behaviour
and
performance
of
materials.
Density
is
defined
a
the
mass
to
volume
ratio
of
a
material,
or
alternatively,
the
mass
of
a
substance
that
occupies
a
unit
volume.
Calculation
of
density
appears
straightforward:
Density
=
Mass
/
Volume.
However,
depending
on
the
precise
volume
measurement,
different
representations
of
density
can
be
calculated,
which
often
differ
in
both
their
absolute
value,
their
representation
of
the
sample material and relationship with material properties and performance.
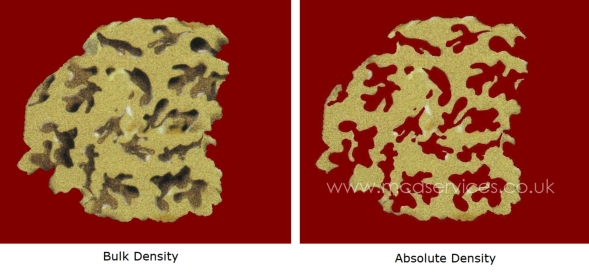
Bulk
Density,
also
termed
envelope
density,
includes
the
volume
of
all
pores
within
the
sample.
At
MCA
Services
this
is
measured
by
mercury
displacement
using
out
Micromeritics
AutoPore
V
instrument
and
is
available
as
a
stand-alone
analytical
option
or
as
part
of
the
more
comprehensive mercury porosimetry options.
Absolute
Density,
also
termed
true
density,
excludes
the
volume
of
all
open
pores
within
the
sample
and,
therefore,
represents
the
density
of
just
the
solid
material.
The
standard
method
used
at
MCA
Services
is
gas
pycnometry
by
helium
displacement
using
our
Micromeritics
AccuPyc
instrument.
If
helium
entrapment
is
of
concern
options
for
using
nitrogen
are also available.
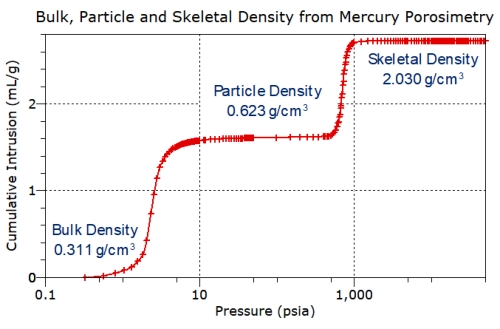
Bulk
density
calculation
is
included
in
all
of
our
mercury
porosimetry
options,
which
also
provide
pore
volume,
pore
size
and
pore
area
distribution
data
in
the
pore
size
range
3.5nm
to
650µm.
Significantly,
skeletal
density
(the
density
of
solid
material,
excluding
all
open
pores
<3.5
nm)
and
absolute
porosity
are
also
included
with
these
options.
Furthermore,
with
powder
and
granule
samples
it
is
usually
possible
to
differentiate
between
inter-particulate
and
intra-particulate
porosity,
which
allows
for
the
calculation
of
particle
density.
In
such
cases
bulk
density
represents
the
envelope
volume
of
the
entire
packed
powder
bed,
including
the
volume
of
inter-particulate
spaces
and
particle
density
measures
that
of
the
powder
grains
excluding
the
inter-particulate
volume.
For
helium
pycnometry
analysis,
MCA
Services
has
a
range
of
sample
cells
which
allow
for
the
accurate
determination
of
absolute
density
using
samples
quantities
from
1
cm
3
to
10
cm
3
.
It
is,
therefore,
possible
to
analyse
a
wide
range
of
sample
types,
from
fine
powders
to
larger
solid
pieces.
If
the
theoretical
absolute
density
of
a
sample
material
is
known
it
is
also
possible
to
calculate
the
volume
of
closed
pores
within
the
sample
from
the
helium
pycnometry
value.
Such
calculation
is
especially
useful
when
considering
foam
and
construction
materials
as
it
represents the void volume within the sample material.
Density Measurement – Pycnometry
Bulk / Envelope Density Measurement
Absolute / True Density Measurement
Skeletal & Particle Density Measurement
Density
is
an
important
physical
characteristic
of
solid
materials,
which
has
inextricable
links
to
porosity
and
direct
affects
the
behaviour
and
performance
of
materials.
Density
is
defined
a
the
mass
to
volume
ratio
of
a
material,
or
alternatively,
the
mass
of
a
substance
that
occupies
a
unit
volume.
Calculation
of
density
appears
straightforward:
Density
=
Mass
/
Volume.
However,
depending
on
the
precise
volume
measurement,
different
representations
of
density
can
be
calculated,
which
often
differ
in
both
their
absolute
value,
their
representation
of
the
sample
material
and
relationship
with
material
properties
and
performance.
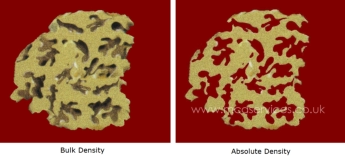
Bulk
Density,
also
termed
envelope
density,
includes
the
volume
of
all
pores
within
the
sample.
At
MCA
Services
this
is
measured
by
mercury
displacement
using
out
Micromeritics
AutoPore
V
instrument
and
is
available
as
a
stand-alone
analytical
option
or
as
part
of
the
more
comprehensive
mercury
porosimetry options.
Absolute
Density,
also
termed
true
density,
excludes
the
volume
of
all
open
pores
within
the
sample
and,
therefore,
represents
the
density
of
just
the
solid
material.
The
standard
method
used
at
MCA
Services
is
gas
pycnometry
by
helium
displacement
using
our
Micromeritics
AccuPyc
instrument.
If
helium
entrapment
is
of
concern
options
for
using
nitrogen
are
also avai
lable.
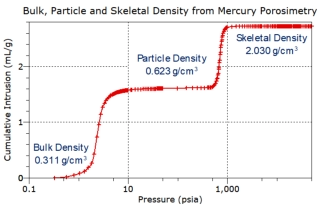
Bulk
density
calculation
is
included
in
all
of
our
mercury
porosimetry
options,
which
also
provide
pore
volume,
pore
size
and
pore
area
distribution
data
in
the
pore
size
range
3.5nm
to
650µm.
Significantly,
skeletal
density
(the
density
of
solid
material,
excluding
all
open
pores
<3.5
nm)
and
absolute
porosity
are
also
included
with
these
options.
Furthermore,
with
powder
and
granule
samples
it
is
usually
possible
to
differentiate
between
inter-particulate
and
intra-particulate
porosity,
which
allows
for
the
calculation
of
particle
density.
In
such
cases
bulk
density
represents
the
envelope
volume
of
the
entire
packed
powder
bed,
including
the
volume
of
inter-particulate
spaces
and
particle
density
measures
that
of
the
powder
grains
excluding
the
inter-
particula
te volume.
For
helium
pycnometry
analysis,
MCA
Services
has
a
range
of
sample
cells
which
allow
for
the
accurate
determination
of
absolute
density
using
samples
quantities
from
1
cm
3
to
10
cm
3
.
It
is,
therefore,
possible
to
analyse
a
wide
range
of
sample
types,
from
fine
powders
to
larger
solid
pieces.
If
the
theoretical
absolute
density
of
a
sample
material
is
known
it
is
also
possible
to
calculate
the
volume
of
closed
pores
within
the
sample
from
the
helium
pycnometry
value.
Such
calculation
is
especially
useful
when
considering
foam
and
construction
materials
as
it
represents the void volume within the sample material.
















