Expertise in the Physical
Characterisation of Materials

MCA Services
Unit 1A Long Barn, North End, Meldreth, Cambridgeshire SG8 6NT UK
01763 262333
© MCA Services




Analysis of Catalysts and Electro-catalyst Systems
The
significance
and
influence
of
the
porous
nature
of
catalyst
systems
with
respect
to
their
functionality,
performance
and
efficiency
is
well
known
as
is
the
importance
of
understanding
the
physicochemical
properties
of
the
active
constituents.
The
characterisation
of
the
porous
nature
of
catalysts
can
be
applied
to
the
active
constituents
and
supports
separately
or
to
the
finished
system.
These
principles
can
also
be
applied
to
electro-catalyst
systems
and
our
Battery
Materials
page
gives
more
details.
Investigations
of
physicochemical
properties
in
order
to
determine
activity
and
efficiency
can
also
be
applied
to
the
active
constituents
alone
or
to
the
finished
catalytic
system.
All
of
these
properties
can
not
only
be
applied
to
new
catalysts
but
also
to
used
and
regenerated
materials
as
part
of
investigations
into
their
degradation and regeneration efficiency.
Key Techniques.
•
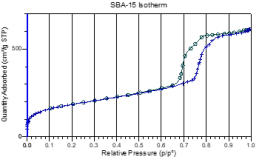
Gas Adsorption: pore size, area and volume determination in the mesopore
range.
•
Gas Adsorption: BET Surface Area.
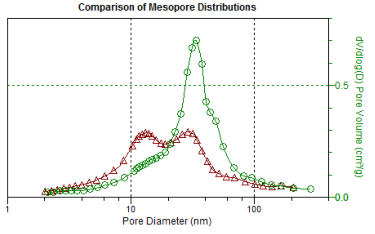
•
Micropore Analysis: pore size, area and volume determination in the micropore
range.
•
Micropore Analysis: wide choice of adsorbate gases for ultra-micropore
characterisation.
•
Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry: pore size, area and volume determination in
meso & macropore ranges.
•
Mercury Intrusion / Extrusion Porosimetry: cavity to throat size
determination.
•
Chemisorption: active metal surface area and dispersion measurement.
•
Permeability and Tortuosity: measurement by mercury intrusion
porosimetry.
•
Temperature Programmed Methods: reduction, oxidation, adsorption &
desorption.
•
Density Measurement: absolute density, bulk (envelope) density and skeletal density.
MCA
Services
offers
a
complete
suite
of
techniques
for
the
physical
characterisation
of
catalyst
systems.
Through
Mercury
porosimetry
and
gas
adsorption
with
micropore
analysis,
the
complete
range
of
pore
sizes,
from
micropores,
through
mesopores
and
into
macropores
can
be
characterised
for
volume,
area
and
pore
size
distributions.
The
complete
range
of
pore
sizes
which
can
be
measured
by
combination
of
these
techniques
is
in
the
order
of
3
nm
to
650
µm.
Gas
adsorption
options
usually
also
provide
the
BET
surface
area
of
the
sample
material
as
part
of the analysis. Mercury porosimetry options can be extended to include the measurement of permeability and pore tortuosity.
Whilst
nitrogen
is
traditionally
applied
to
gas
adsorption,
more
specialised
adsorbate
options
are
available
for
the
analysis
of
specific
sample
materials.
For
example,
characterisation
of
ultra-micropores
(<
1.0
nm)
in
carbon,
charcoal,
graphene,
CNTs
etc
can
be
analysed
by
carbon
dioxide
adsorption
whilst
argon
adsorption
is
preferred
when
analysing
zeolites,
MOFs
and
ZIFs.
Hydrogen,
oxygen
and
water
adsorption
options are also available as is the measurement of the isosteric heat of adsorption from hydrogen isosteres.
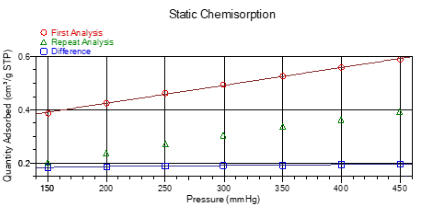
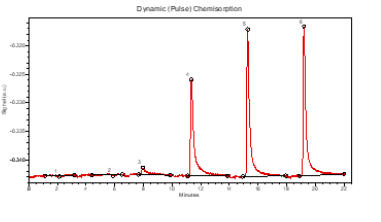
Chemisorption
(chemical
adsorption)
is
routinely
applied
to
the
analysis
of
a
ctive
metal
constituents
to
determine
their
availability
for
the
desired
catalytic
reaction.
The
active
metal
surface
area
and
active
metal
dispersion
are
most
commonly
applied
to
this.
At
MCA
Services
we
offer
chemisorption
by
static
volumetric
and
dynamic
(pulse)
techniques
and
the
provision
of
a
range
of
sorptive
gases
means
that
a
wide
range
of
active
metals
of
varying
loading
can
be
analysed.
Hydrogen
and
carbon
monoxide
chemisorption
represent
the
most
common
methods
but
other sorptive gases are available, such as ammonia and oxygen.
We
have
extensive
experience
in
the
field
of
catalysis
and
the
expertise
to
assist
with
the
interpretation
of
results
to
gain
the
maximum
insight
into
the
materials
analysed.
Benefits
are
extended
through
the
application
of
state-of-the-art instrumentation and software which provide the highest quality results together with specialised reporting options.






Expertise in the Physical
Characterisation of Materials
MCA Services
Unit 1A Long Barn, North End,
Meldreth, Cambridgeshire SG8 6NT UK
01763 262333
© MCA Services




Analysis of Catalysts and Electro-catalyst Systems
The
significance
and
influence
of
the
porous
nature
of
catalyst
systems
with
respect
to
their
functionality,
performance
and
efficiency
is
well
known
as
is
the
importance
of
understanding
the
physicochemical
properties
of
the
active
constituents.
The
characterisation
of
the
porous
nature
of
catalysts
can
be
applied
to
the
active
constituents
and
supports
separately
or
to
the
finished
system.
These
principles
can
also
be
applied
to
electro-catalyst
systems
and
our
Battery
Materials
page
gives
more
details.
Investigations
of
physicochemical
properties
in
order
to
determine
activity
and
efficiency
can
also
be
applied
to
the
active
constituents
alone
or
to
the
finished
catalytic
system.
All
of
these
properties
can
not
only
be
applied
to
new
catalysts
but
also
to
used
and
regenerated
materials
as
part
of
investigations
into
their
degradation
and
regeneration efficiency.
Key Techniques.
Gas Adsorption: pore size, area and volume determination in the
mesopore range.
Gas Adsorption: BET Surface Area.
Micropore Analysis: pore size, area and volume determination in the
micropore range.
Micropore Analysis: wide choice of adsorbate gases for ultra-
micropore characterisation.
Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry: pore size, area and volume
determination in meso & macropore ranges.
Mercury Intrusion / Extrusion
Porosimetry: cavity to throat
size determination.
Chemisorption: active metal
surface area and dispersion
measurement.
Permeability and Tortuosity:
measurement by mercury intrusion porosimetry.
Temperature Programmed Methods: reduction, oxidation, adsorption
& desorption.
Density Measurement: absolute density, bulk (envelope) density and
skeletal density.
MCA
Services
offers
a
complete
suite
of
techniques
for
the
physical
characterisation
of
catalyst
systems.
Through
Mercury
porosimetry
and
gas
adsorption
with
micropore
analysis,
the
complete
range
of
pore
sizes,
from
micropores,
through
mesopores
and
into
macropores
can
be
characterised
for
volume,
area
and
pore
size
distributions.
The
complete
range
of
pore
sizes
which
can
be
measured
by
combination
of
these
techniques
is
in
the
order
of
3
nm
to
650
µm.
Gas
adsorption
options
usually
also
provide
the
BET
surface
area
of
the
sample
material
as
part
of
the
analysis.
Mercury
porosimetry
options
can
be
extended
to
include
the
measurement
of
permeability
and
pore
tortuosity.
Whilst
nitrogen
is
traditionally
applied
to
gas
adsorption,
more
specialised
adsorbate
options
are
available
for
the
analysis
of
specific
sample
materials.
For
example,
characterisation
of
ultra-micropores
(<
1.0
nm)
in
carbon,
charcoal,
graphene,
CNTs
etc
can
be
analysed
by
carbon
dioxide
adsorption
whilst
argon
adsorption
is
preferred
when
analysing
zeolites,
MOFs
and
ZIFs.
Hydrogen,
oxygen
and
water
adsorption
options
are
also
available
as
is
the
measurement
of
the
isosteric heat of adsorption from hydrogen isosteres.
Chemisorption
(chemical
adsorption)
is
routinely
applied
to
the
analysis
of
active
metal
constituents
to
determine
their
availability
for
the
desired
catalytic
reaction.
The
active
metal
surface
area
and
active
metal
dispersion
are
most
commonly
applied
to
this.
At
MCA
Services
we
offer
chemisorption
by
static
volumetric
and
dynamic
(pulse)
techniques
and
the
provision
of
a
range
of
sorptive
gases
means
that
a
wide
range
of
active
metals
of
varying
loading
can
be
analysed.
Hydrogen
and
carbon
monoxide
chemisorption
represent
the
most
common
methods
but
other
sorptive
gases
are
available,
such
as
amm
onia and oxygen.
We
have
extensive
experience
in
the
field
of
catalysis
and
the
expertise
to
assist
with
the
interpretation
of
results
to
gain
the
maximum
insight
into
the
materials
analysed.
Benefits
are
extended
through
the
application
of
state-of-the-art
instrumentation
and
software
which
provide
the
highest
quality
results
together
with
specialised reporting options.


01763262333